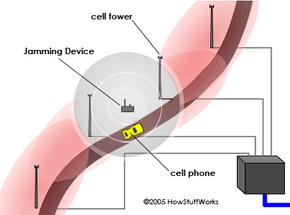
In the United States, United Kingdom, Australia and many other countries, blocking cell-phone services (as well as any other electronic transmissions) is against the law. In the United States, cell-phone jamming is covered under the Communications Act of 1934, which prohibits people from "willfully or maliciously interfering with the radio communications of any station licensed or authorized" to operate. In fact, the "manufacture, importation, sale or offer for sale, including advertising, of devices designed to block or jam wireless transmissions is prohibited" as well.
Jamming is seen as property theft, because a private company has purchased the rights to the radio spectrum, and jamming the spectrum is akin to stealing the property the company has purchased. It also represents a safety hazard because jamming blocks all calls in the area, not just the annoying ones. Jamming a signal could block the call of a babysitter frantically trying to contact a parent or a someone trying to call for an ambulance.
The Federal Communications Commission is charged with enforcing jamming laws. However, the agency has not yet prosecuted anyone for cell-phone jamming. Under the U.S. rules, fines for a first offense can range as high as $11,000 for each violation or imprisonment for up to one year, and the device used may also be seized and forfeited to the government.
In most countries, it is illegal for private citizens to jam cell-phone transmission, but some countries are allowing businesses and government organizations to install jammers in areas where cell-phone use is seen as a public nuisance. In December 2004, France legalized cell-phone jammers in movie theaters, concert halls and other places with performances. France is finalizing technology that will let calls to emergency services go through. India has installed jammers in parliament and some prisons. It has been reported that universities in Italy have adopted the technology to prevent cheating. Students were taking photos of tests with their camera phones and sending them to classmates.
With phones ringing in movies, weddings and classrooms, it's no wonder people want to tone down the intrusion. So what legally can be done to stop annoying cell-phone use?