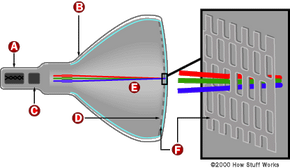
The history of television, often abbreviated as "TV," is a journey through innovation, beginning with mechanical scanning systems and evolving into the modern televisions we know today.
Early Days
This journey began in earnest with the first demonstration of moving images using a spinning Nipkow disk, a rudimentary form of mechanical scanning. However, it was Philo Farnsworth's image dissector that marked a pivotal moment in television technology. Farnsworth's invention, which was showcased in a public demonstration, utilized a new technology that captured moving images without the need for mechanical parts, paving the way for the electronic television.
In the early stages, the TV screen size was quite small, with a flickering image that left much to be desired. Despite these limitations, the excitement around the ability to broadcast moving images through radio waves captured the imagination of viewers.
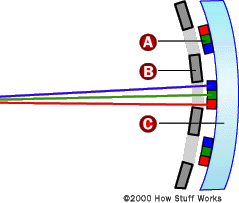
Regular television broadcasts soon became a reality, initially reaching a limited number of people due to the scarce availability of high-end TVs. The Farnsworth television, named after its inventor, stood out for its use of the image dissector, which allowed for clearer pictures than the spinning disk systems.
Modern Television
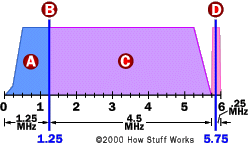
As television technology advanced, so did the quality and features of the TV sets. The screen size increased, offering viewers a more immersive experience. Modern televisions now boast operating systems that support a wide range of applications, from streaming film and TV shows to browsing the internet, all delivered with clarity and precision that far exceeds the European standard of earlier days.
From the abbreviation "TV" to terms like "radio" and "broadcast," the lexicon surrounding television reflects its roots in radio waves and its evolution into a ubiquitous form of entertainment and information. Today, most people have access to a variety of systems, including high-end TVs that offer not just content but a gateway into a world of interactive media, thanks to ongoing innovations in television technology.